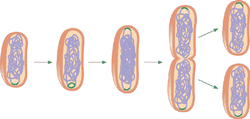
Binary fission occurs within a cell as a axesual way of reproduction.
It happens only in prokaryotes. The cell divides in two approximatly
equal parts. The cell replicate its DNA and one copy of its origin DNA moves towards
the other end of the cell. Once replication is complete, the plasma membrane grows inward and a new cell wall is made. The result is two daughter cells.
Bacteria also reproduce with exchange of genetic informations. It is similar to sexual reproduction as it is a blending of genes between two organisms.
There is three way in which the bacteria can exchange genetic informations.
It happens only in prokaryotes. The cell divides in two approximatly
equal parts. The cell replicate its DNA and one copy of its origin DNA moves towards
the other end of the cell. Once replication is complete, the plasma membrane grows inward and a new cell wall is made. The result is two daughter cells.
Bacteria also reproduce with exchange of genetic informations. It is similar to sexual reproduction as it is a blending of genes between two organisms.
There is three way in which the bacteria can exchange genetic informations.
- Conjugation: A male sex pilus passes DNA to a female cell.
- Transformation: The bacteria takes DNA from dead bacteria
- Transduction: Bacteriophages carries DNA from one cell to another
Four growth phase
Within the time the bacteria is living, it undergoes four different growth phase.
Within the time the bacteria is living, it undergoes four different growth phase.
- Lag phase: This is when the bacteria is maturing and not yet able to divide.
- Log phase: This is when the cells are doubling. The rate of the growth depends of the conditions it's growing in. It can't go on indefinitely as the nutriments become sparse and the waste concentration grows.
- Stationary phase: This is when the growth rate and death rate are equal. It often happen in presence of growth limiting factors such as depletion of an essential nutriment.
- Death phase: This is when bacteria dies. It could be from lack of nutriments, too high or too low temperatures or wrong living conditions.